Causes and Symptoms of Brain Hemorrhage
A brain hemorrhage is a type of stroke. It's caused by an artery in the brain bursting and causing localized bleeding in the surrounding tissues. This bleeding kills brain cells.
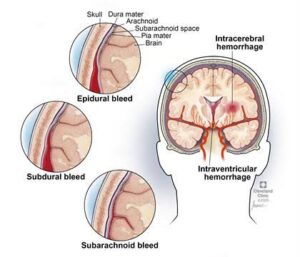
Brain hemorrhages are also called cerebral hemorrhages, intracranial hemorrhages, or intracerebral hemorrhages. They account for about 13% of strokes.
Since some brain hemorrhages can be disabling or life-threatening, it’s important to get medical help fast if you think someone is having one. Here’s what you need to know about the causes, symptoms, and more.
What Happens During a Brain Hemorrhage?
When blood from trauma irritates brain tissues, it causes swelling. This is known as cerebral edema. The pooled blood collects into a mass called a hematoma. These conditions increase pressure on nearby brain tissue, and that reduces vital blood flow and kills brain cells.
Bleeding can occur inside the brain, between the brain and the membranes that cover it, between the layers of the brain's covering or between the skull and the covering of the brain.
What Causes Bleeding in the Brain?
There are several risk factors and causes of brain hemorrhages. The most common include:
Head trauma. Injury is the most common cause of bleeding in the brain for those younger than age 50.
High blood pressure. This chronic condition can, over a long period of time, weaken blood vessel walls. Untreated high blood pressure is a major preventable cause of brain hemorrhages.
Aneurysm. This is a weakening in a blood vessel wall that swells. It can burst and bleed into the brain, leading to a stroke.
Blood vessel abnormalities. (Arteriovenous malformations) Weaknesses in the blood vessels in and around the brain may be present at birth and diagnosed only if symptoms develop.
Amyloid angiopathy. This is an abnormality of the blood vessel walls that sometimes occurs with aging and high blood pressure. It may cause many small, unnoticed bleeds before causing a large one.
Blood or bleeding disorders.
Hemophilia and sickle cell anemia can both contribute to decreased levels of blood platelets and clotting. Blood thinners are also a risk factor.
Liver disease.
This condition is associated with increased bleeding in general.
Brain tumors.
What Are the Symptoms of Brain Bleeding?
The symptoms of a brain hemorrhage can vary. They depend on the location of the bleeding, the severity of the bleeding, and the amount of tissue affected. Symptoms tend to develop suddenly. They may progressively worsen.
If you exhibit any of the following symptoms, you may have a brain hemorrhage. This is a life-threatening condition, and you should call 911 or go to an emergency room immediately. The symptoms include:
A sudden severe headache
Seizures with no previous history of seizures
Weakness in an arm or leg
Nausea or vomiting
Decreased alertness; lethargy
Changes in vision
Tingling or numbness
Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
Difficulty swallowing
Difficulty writing or reading
Loss of fine motor skills, such as hand tremors
Loss of coordination
Loss of balance
An abnormal sense of taste
Loss of consciousness
Keep in mind that many of these symptoms are often caused by conditions other than brain hemorrhages.
Can Brain Hemorrhages Be Prevented?
Because the majority of brain hemorrhages are associated with specific risk factors, you can minimize your risk in the following ways:
Treat high blood pressure. Studies show that 80% of cerebral hemorrhage patients have a history of high blood pressure. The single most important thing you can do is control yours through diet, exercise, and medication.
Don’t smoke.
Don’t use drugs. Cocaine, for example, can increase the risk of bleeding in the brain.
Drive carefully, and wear your seat belt.
If you ride a motorcycle, bicycle or skateboard, always wear a helmet.
Investigate corrective surgery. If you suffer from abnormalities, such as aneurysms, surgery may help to prevent future bleeding.
Be careful with warfarin (Coumadin). If you take this blood-thinning drug follow up regularly with your doctor to make sure your blood levels are in the correct range.
|
ReplyForward
|
